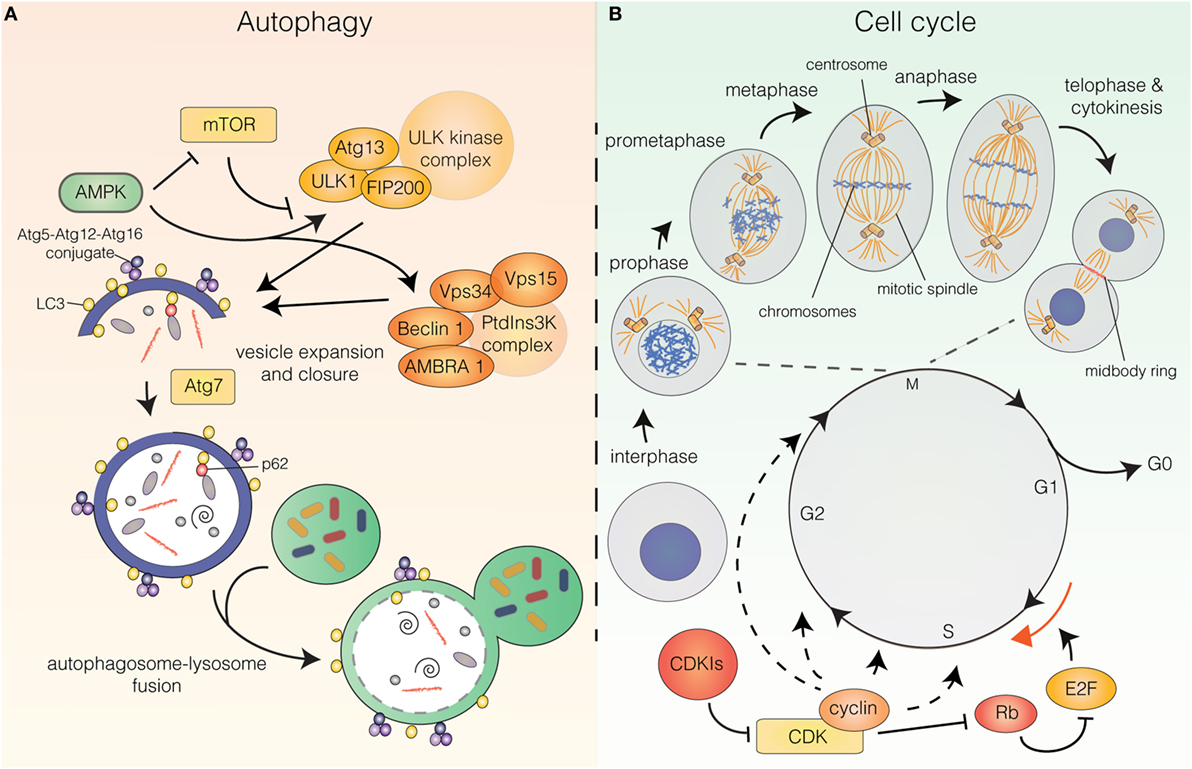
Cellular Responses to PlatinumBased Anticancer Biology Diagrams
Cellular Responses to PlatinumBased Anticancer Biology Diagrams Furthermore, the formation of doxorubicin-DNA adducts could activate DNA damage responses independent of topoisomerase II. 8 When cells experience DNA damage, the cell cycle can be arrested in the G1, S or G2 phase for DNA repair. 9 If the DNA damage is beyond recovery or the level of double-stranded breaks exceeds the repair capacity, cells
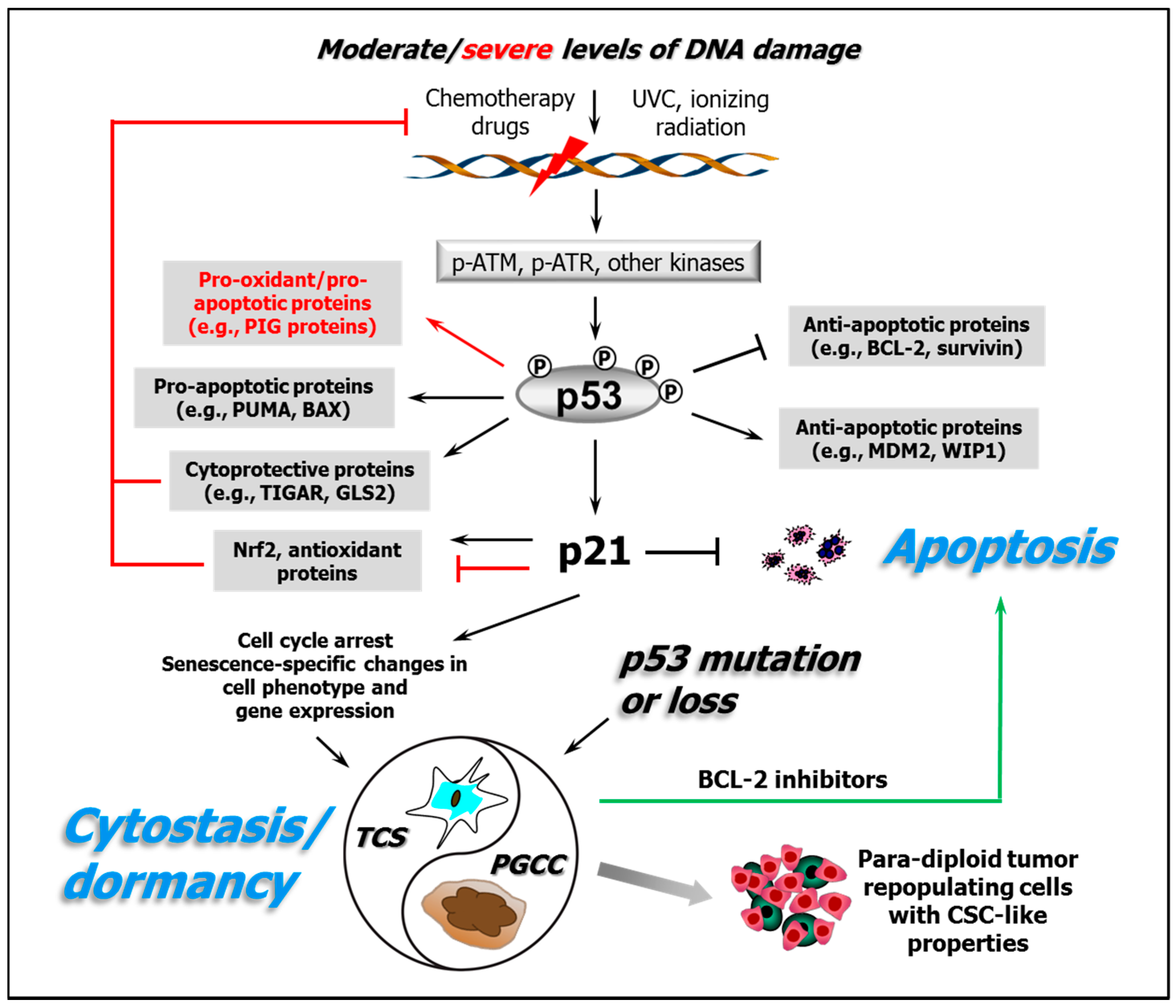
Generating excessive levels of DNA damage, through either radiotherapy or chemotherapy, The cell-cycle arrest and apoptotic functions of p53 in tumor initiation and progression.

Targeting Control of Cell Cycle Enhances the Activity of Conventional ... Biology Diagrams
Impairment of caspase activity using pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD reveals this chemotherapy-induced apoptotic pathway as an essential factor in driving synergy. Mannose-6-phosphate receptor-mediated autophagy and the arrest of cell cycle in G2/M are also shown to be induced by chemotherapy and significantly contributing to the synergy. Keywords: cell cycle arrest, DNA damage, chemotherapy. Introduction. The normal cell cycle consists of complex pathways that regulate the duplication of all molecules and organelles and their separation into two identical daughter cells. This progresses through four phases: G1 (gap), S (synthesis), G2 (gap) and M (mitosis) and is coordinated by
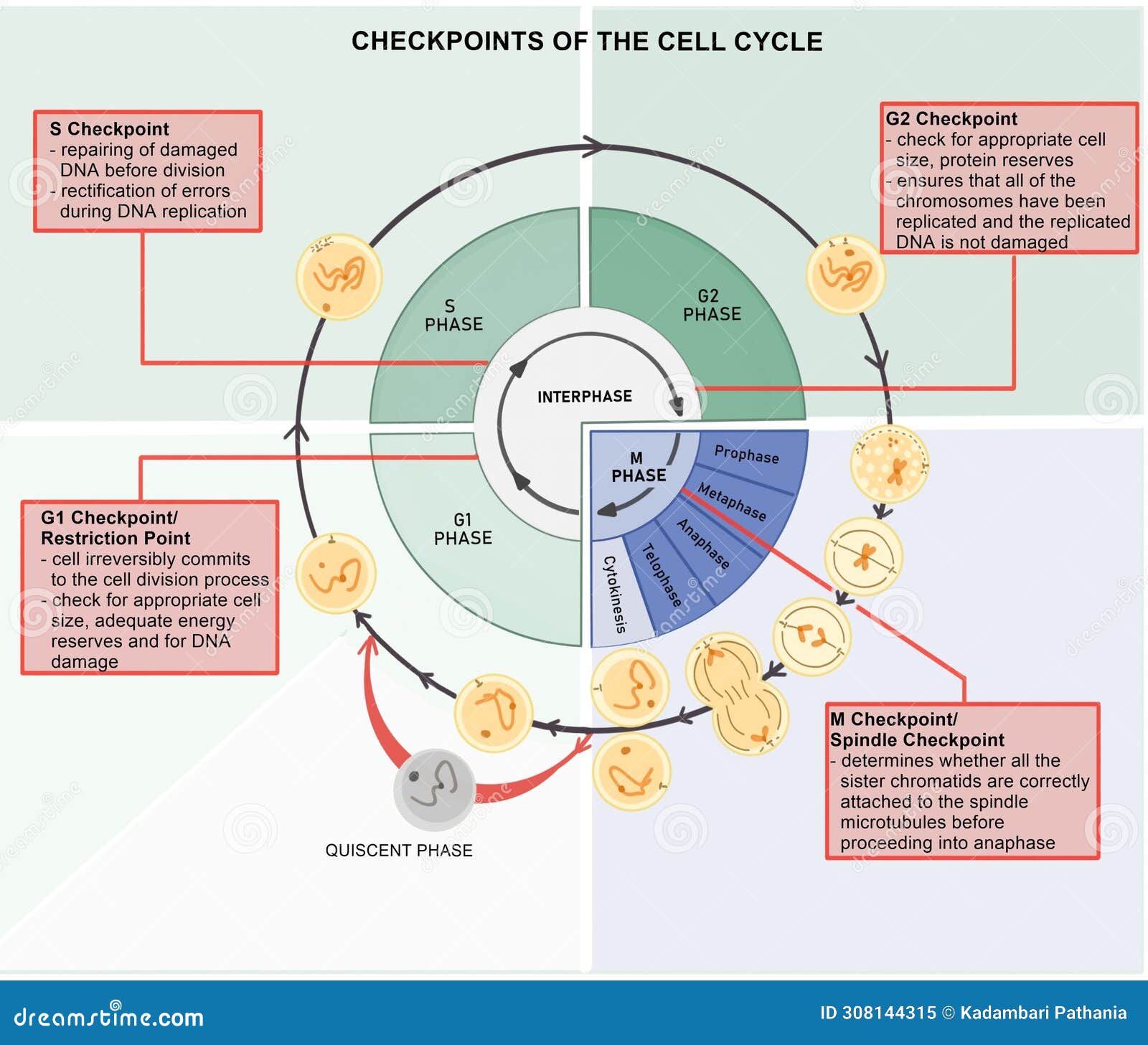
In preclinical studies, it was reported to induce cell cycle arrest and tumor growth inhibition in a majority of solid tumor cell lines especially those of B-cell origin and xenografts 88. phase II clinical trials were completed with flavopiridol in chronic lymphocytic leukemia 89, endometrial adenocarcinoma 90, multiple myeloma 91, and

Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology Biology Diagrams
In conclusion, our data identifies cell cycle dysregulation as a clinically relevant mediator of chemoresistance in AML, highlights therapeutic pitfalls in inducing cell cycle arrest and finally The p53 protein is the product of mutations in the p53 gene. It plays an anti-proliferative effect in different types of stress responses, including cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. For example, when cells are damaged or cell proliferation is abnormal, the p53 gene is activated, leading to cell cycle arrest and even cell apoptosis . In tumor